Describe the Functions of the Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is located in the diencephalon region of the forebrain directs a number of needed functions in the body and is the control center for several autonomic functions. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.

Hypothalamus Function Location What Does The Hypothalamus Do Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Functions of the hypothalamus.

. Heart rate and arterial blood pressure. Together they allow the very small hypothalamus to be the regulator of a wide variety of functions. Start studying 7 Functions of Hypothalamus.
It responds to a variety of internal and external signals of the body via the nervous system. Estrogen targets all of the major hypothalamic neuroendocrine and autonomic cellular groups to activate multiple. THALAMUS The thalamus is believed to both process sensory information as well as relay.
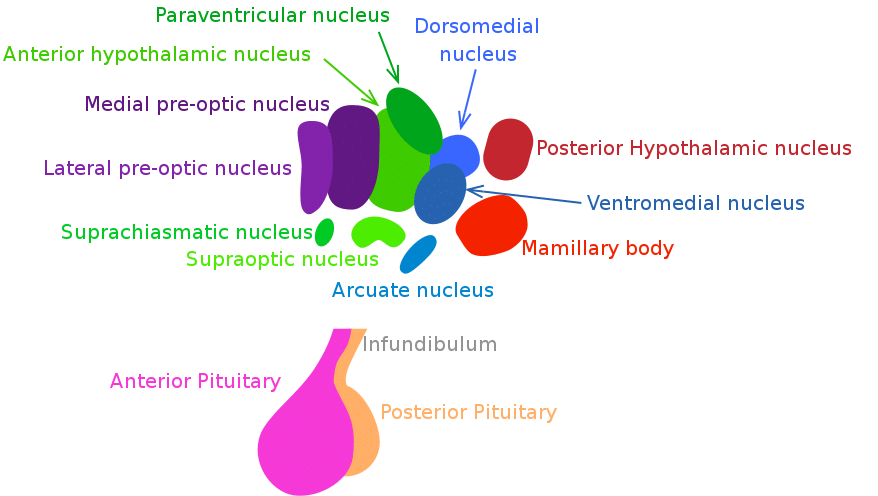
Functions The different nuclei described earlier each have specific functions. It controls the blood pressure the levels of circulating hormones body temperature hunger thirst sleep and emotional activity. Control of hunger and body weight.
Describe the role of the hypothalamus in control of the autonomic nervous system It regulates smooth and cardiac muscle and secretion from glands. The preoptic nucleus of the preoptic region modulates the secretion of gonadotropin releasing hormone which is necessary for sexual reproduction. Anterior circadian rhythms water balance heat dissipation reproduction tuberal endocrine function appetite metabolism and posterior heat generation The hypothalamus can be divided into three longitudinal divisions.
Production of hormones that stimulate the pituitary gland to secrete pituitary hormones. Thus when the hypothalamus doesnt work properly it can cause organic problems that can lead to many disorders. The thalamus hypothalamus and pineal gland are a part of diencephalon.
In addition it helps stimulate many important processes. The hypothalamus controls and coordinates much of your bodys involuntary functions like temperature regulation hunger thirst sleep and mood. A major role of the thalamus is.
By acting in response to input from the brain and from other hormone-producing centers in the body the hypothalamus adjusts the bodys internal balance or homeostasis. The main function of the hypothalamus is to maintain the homeostasis of the body. It regulates primitive functions of the body ranging from water balance and thermoregulation to sex drive and childbirth.
It also plays an important role in regular sleep and wakefulness. The hypothalamus is a small but crucial part of the brain. The hypothalamus is an area of the brain that has many functions despite its small size.
These functional controls include. It controls functions such as sleep and growth. First the hypothalamus receives internal stimuli via receptors for circulating hormones.
It also modulates the endocrine system through its connections with the pituitary gland. Axons extend from the hypothalamus to the sympathetic and parasympathetic nuclei in the brainstem and spinal cord allowing regulation of visceral activities including heart rate movement of food through the GI tract and. Each of the primary sensory relay area receives strong feedback connection from the cerebral cortex.
Summary of the hypothalamus functions. Start studying Phys 7 major functions of the hypothalamus. Many of its functions are carried out by way of the pituitary gland.
The hypothalamus forms the floor and walls of the third ventricle of the brain. Estrogen has multifaceted effects on the hypothalamus that regulate a number of homeostatic functions including reproduction temperature energy balance stress and motivated behaviors. It plays an important role in the production of hormones.
1cardiovascular regulationStimulation in lateral and posterior hypothalamus causes increase in heart rate and increase in arterial pressure whereas stimulation of preoptic area produce opposite ef. View a 3-D diagram and learn about related conditions. Speaking broadly the hypothalamus is a high-level sensory integration and motor output area that maintains homeostasis by controlling endocrine autonomic and somatic behavior.
Water and electrolyte balance. Control of movements and glandular secretions of the stomach and intestines. The hypothalamus is involved in different daily activities like eating or drinking in the control of the bodys temperature and energy maintenance and in the process of memorizing and in stress control.
Structure and Function. Autonomic endocrine and motor function control. The functions of the hypothalamus include quite a few activities like maintaining sleep cycles maintaining homeostasis connecting the nervous and endocrine systems balancing body fluids regulating blood pressure and heart rate etc.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.

Hypothalamic Physiological Function The Hypothalamus Plays A Role In Download Scientific Diagram

Comments
Post a Comment